2024-12-12
Converter is an important device in power electronics, mainly used for the conversion between different types of electrical energy. The types of converters can be divided into different types according to the way of energy conversion, the form of input and output, and the functional requirements. The following are common converter types
AC/DC converter (A
C-DC converter) : Also known as Rectifier (Rectifier) : converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). Common types are single-phase rectifiers, three-phase rectifiers, full-wave rectifiers, etc. Commonly used: DC power supply, motor control, charging system, power transmission, etc.
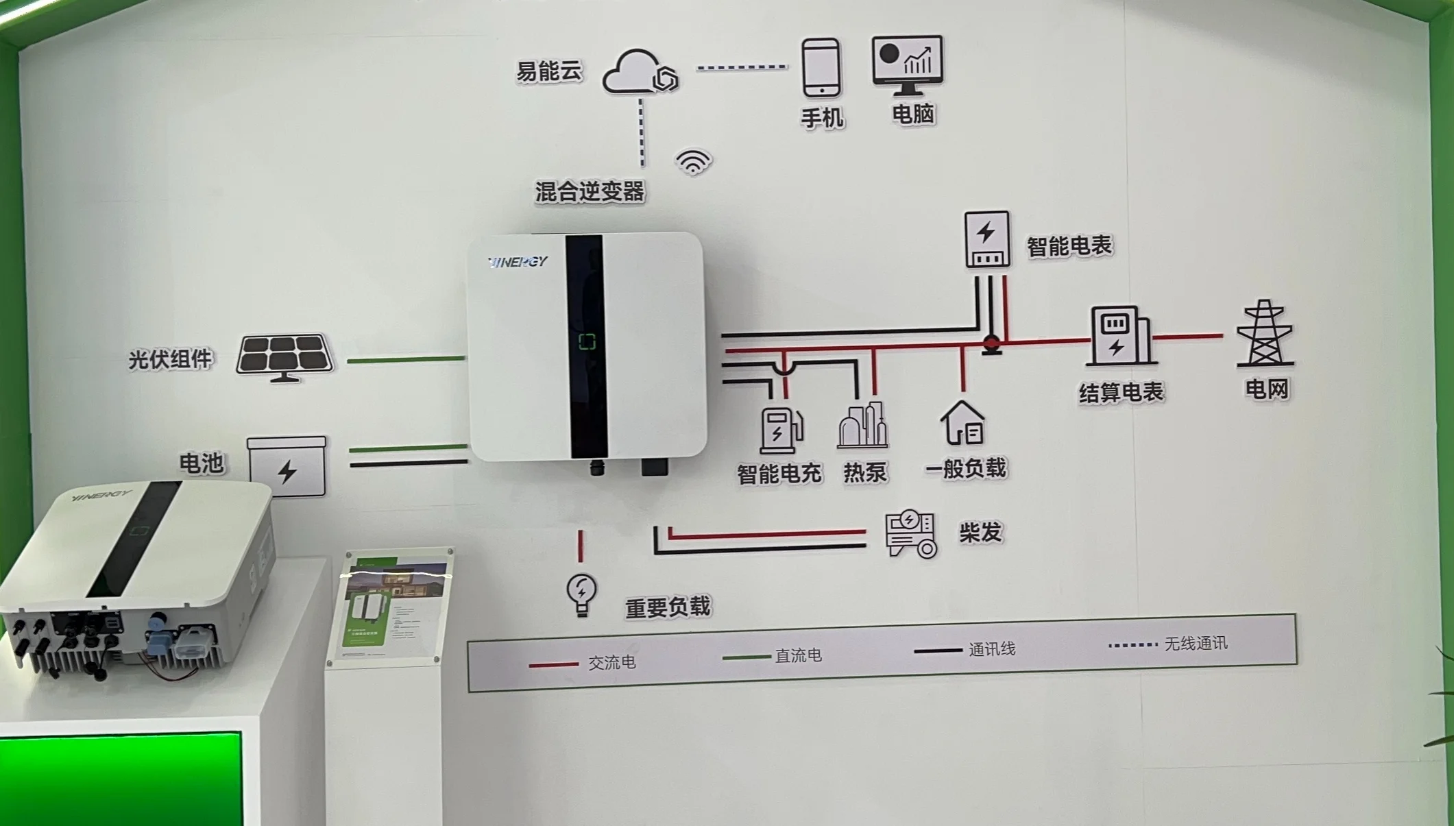
We usually call the Inverter (Inverter) : converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). Common types are square wave inverters, sine wave inverters, rectangular wave inverters and so on. Commonly used in photovoltaic power generation systems, electric vehicles, UPS uninterruptible power supplies, wind power generation and so on.
converter)
Contains a Boost Converter (Boost Converter) : the lower DC voltage will be raised, Buck Converter (Buck Converter), buck boost converter (Buck Boost Converter), can achieve both boost and buck function. Commonly used in battery management systems, power transmission, LED driver
power, mobile devices, etc.
Frequency Converter: Used to change the frequency of alternating current, usually with a combination of rectifier and inverter. Phase-control Converter: Control the Phase Angle of alternating current to adjust the output voltage. Application scenarios: motor speed regulation, frequency conversion in power system, adjustable power supply, etc.
Unidirectional converters, bidirectional converters, bidirectional AC/DC converters (V2G systems for electric vehicles), bidirectional DC/DC converters (battery charging and discharging systems), etc.
Linear Converter: Smooth conversion by adjusting the working state of the switch, usually less efficient, but stable output. Switching converters: Control current and voltage through switching elements (such as transistors) for high efficiency and high power applications.
Pulse width modulation (PWM) converter: The output voltage and current are adjusted by controlling the pulse width of the switching element. Widely used in DC/AC inverters and DC/DC converters.
Resonant Converter: Control the working state of the switching device through the resonant circuit, which can provide higher efficiency and lower EMI (electromagnetic interference).
Multiphase converters: The use of multiple parallel converters to improve system stability and output performance, often used in high-power systems.
Photovoltaic converter: inverter designed for solar photovoltaic power generation system, mainly used to convert direct current generated by photovoltaic panels into alternating current, connected to the grid.
Wind converter: Converts direct current or alternating current generated by a wind power generation system into electrical energy suitable for transmission to the grid.
Electric vehicle charging converter: The converter in the charging pile is used to convert alternating current in the grid to direct current suitable for charging electric vehicle batteries, or for battery reverse discharge to provide power to the grid.
UPS uninterruptible power supply converters: To ensure the stability of the power system, the converters in the UPS system are responsible for providing power protection during power outages or power fluctuations.
Single-stage converter: The energy conversion between input and output is completed in one conversion stage. The structure is simple, but larger switching elements may be required.
Multistage converters: Energy conversion through multiple conversion stages can provide higher efficiency and more stable output, often used in high-power and high-demand scenarios.
At the total price, we commonly use the following types of converters:
3.DC/DC converter: DC/DC conversion, commonly seen in battery management, LED drivers, power transmission, etc.
Each converter type has its own specific design and application scenario, and the right converter is usually selected based on the power, efficiency and control strategy required.